
Hair loss can be devastating and the mere thought of hair loss is enough to drive some individuals up the wall. Hair loss sufferers will never forget the first time they heard the dreaded question "are you going bald?". Although most individuals brush it off in the beginning as a mistake or fluke, the reality doesn't take long to sink in.
Most blame their thinning thatch on a bad haircut, lighting, stress or any other excuse in the sun before admitting the culprit; genetic hair loss. So how do you know if you're going bald? In this article, we will go over the first signs of hair loss, as well as the most effective treatments to reverse hair loss.
The First Signs Of Hair Loss and How To Spot It

Hair loss is a gradual process of miniaturization. The hair follicles are gradually degraded by the hormone DHT. The hormone DHT binds to the androgen receptor sites in the hair follicle and slowly begins to shrink the hair follicles until they no longer grow. However, this process doesn't happen overnight.
In fact, most individuals have lost approximately 50% of their hair before they even notice any hair loss. This is why it is imperative to remain vigilant because the sooner the hair loss is treated the more hair can be saved.
In the beginning, hair loss is contained in the frontal areas of the scalp, specifically the hairline. As the hair loss progresses, the hairline recedes further into the midsection of the scalp. Shortly after, the crown (vertex) begins to thin and expand until it eventually meets the recession in the front of the scalp causing complete baldness.
When an individual is first experiencing hair loss it may be difficult to see, because in most situations the individual will appear to have a full head of hair. However, there are certain situations that could reveal the hair loss.
The most effective way of seeing the first signs of hair loss is by taking photographs under bright lights to expose any differences in density. Individuals who are not suffering from hair loss will not have any visible differences in density. However, someone who is suffering from hair loss will see a visible change in density.
Additionally, taking pictures with wet hair may reveal a male pattern or female pattern hair loss, which follows a distinct pattern. This is especially helpful for individuals who suffer from Diffuse Patterned Alopecia (DPA).
DPA is a form of genetic hair loss that causes a total diffuse thinning, as opposed to the gradual recession.
The Most Effective Treatments That Can Reverse and Regrow Hair
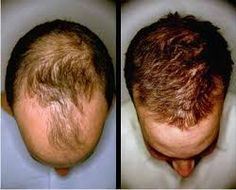
Unfortunately, there is no cure for androgenic alopecia (genetic hair loss), the available treatments today can prevent, slow and some cases even regrow hair. That said, the treatments must be maintained in order to continually reap the benefits.
Rogaine (minoxidil): Minoxidil is a topical hair loss solution that is applied topically twice per day. Although, the exact mechanism of how minoxidil works is relatively unknown. Many believe that minoxidil works by prolonging the anagen (growth) phase of the hair follicle and by thickening the hair shaft diameter. Thus, providing the appearance of a fuller head of hair.
Rogaine (minoxidil) was the first hair loss medication that was approved by the FDA.
Propecia (finasteride): Finasteride is the only anti-androgen medication that has been approved by the FDA to treat hereditary hair loss. Finasteride works by inhibiting the 5-alpha reductase enzyme. The 5-alpha reductase enzyme is responsible for converting testosterone in to DHT through the bloodstream. Therefore, by inhibiting the 5-alpha reductase enzyme finasteride is able to reduce up to 70% of DHT serum in the body. To date, finasteride is the most effective medication for the treatment of genetic hair loss.
Nizoral (ketoconazole) shampoo: While the FDA has not approved any shampoo for the treatment of genetic hair loss, there is some clinical evidence that suggest ketoconazole may be effectivein treating hair loss.
According to clinical studies ketoconazole has been shown to be as effective as 2% minoxidil. While this may not be enough to treat hair loss alone, it is a useful treatment to use as an adjunct to minoxidil and finasteride.
Hair Transplant Surgery: Surgical hair restoration has been around for decades, but many still believe that hair transplants appear the same as they did decades ago. Thankfully, this couldn't be further from the truth. Today, hair transplants when done right are undetectable even under close scrutiny from hairstylists and barbers. To date, hair transplant surgery is the only way to regrow hair on a completely bald scalp. Hair restoration remains the most effective treatment for hair loss.
Conclusion
While there is no cure for androgenic alopecia, the treatments available today are enough to restore the appearance of a full head of hair. Many hair loss sufferers use minoxidil, finasteride and ketoconazole shampoo simultaneously, this combination is referred to as "the big 3".
Many individuals who take the "big 3" and have a hair transplant procedure are able to restore the appearance of fullness and reverse their hair loss.

